Irreversible and Reversible Temperature Equilibration

Description
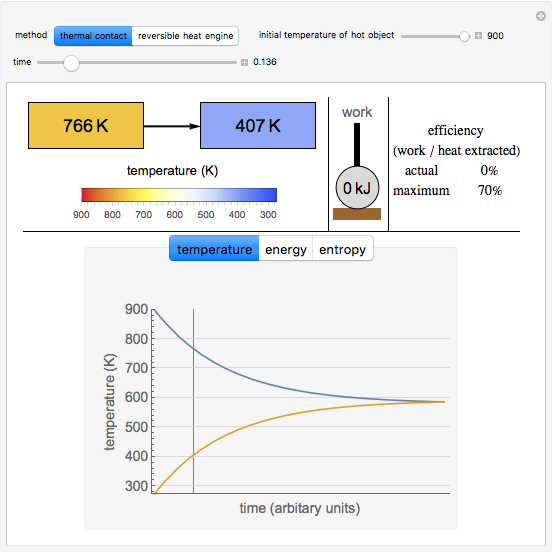
This simulation compares two ways objects at different temperatures can thermally equilibrate: irreversibly through thermal contact and reversibly with an ideal heat engine, utilizing a Carnot cycle. The heat engine converts some of the heat into work and results in a lower final temperature for the two objects than thermal contact. The schematics at the top show the changing temperatures of the two objects, the amount of work performed, and the efficiency of the process. The plots at the bottom show how temperature, energy, and entropy of the objects change. Most of the entropy increase (for thermal contact) or work generation (for the heat engine) occurs near the start of the process, when the temperature difference between the objects is maximum.
About
Author: Tad Hogg. Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA.
View the source code for this simulation
